Hovering with SPACEX 16
A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket launched the Dragon CRS-16 cargo resupply mission to the International Space Station on Dec. 5, 2018.
The SpaceX Falcon 9 was ferrying material for the inauguration of several projects and we are honored to play a role in this mission.


![]() Dr. Vekilov (left) and Mr. Xu (right)
Dr. Vekilov (left) and Mr. Xu (right)
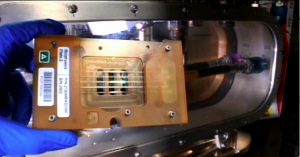
The special liquid cell used for the space station contains protein samples with different concentrations.
Mission Operations Started on LMMBIO-2/5 on January 21,2015
ISS Mission Operations began on January 21, 2019, for the Light Microscopy Module Biology experiment two and five (LMMBIO-2/5). The PI is from the University of Houston (Peter Vekilov). This first phase of the experiment will run two of the five modules. The remaining spares may operate just before SpaceX-18 (June/July 2019). These samples are of medically relevant cancer protein crystals that evolve much larger on ISS. (Ronald Sicker, GRC/MSI 3-6498 and William Meyer, USRA, 3-5011)

Anne McClain installing LMMBIO-2/5 into the LMM
May science beatify the life
